Lyapunov functions are an extremely convenient device for proving that a dynamical system converges.
Author: appliedprobability
Revenue Equivalence
For a number of differing auction settings, we consider the sale of a single item amongst fixed number of auction participants. It is interesting that under a certain game-theoretic construction all these auctions can be seen to be equivalent.
Cross Entropy Method
In the Cross Entropy Method, we wish to estimate the likelihood
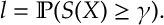
Here is a random variable whose distribution is known and belongs to a parametrized family of densities
. Further
is often a solution to an optimization problem.
Online Convex Optimization
We consider the setting of sequentially optimizing the average of a sequence of functions, so called online convex optimization.
Gradient Descent
We consider one of the simplest iterative procedures for solving the (unconstrainted) optimization
A Network Decomposition
We consider a decomposition of the following network utility optimization problem
SYS:
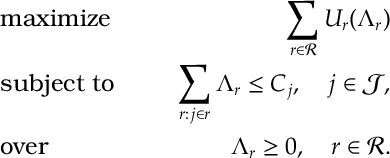
Congestion Control
We argue, in a slightly informal manner, that queueing networks implicitly optimize a utility function subject to constraints on network capacity. We start with the simple example of a closed queueing network and, as we shall discuss, a motivating example is the Transmission Control Protocol which controls the number of packets in transfer on an Internet connection.
Gale-Eisenberg Market
The Gale-Eisenberg is a nice example were the distributed decisions of buyers and sellers have an equilibrium which solves an optimization problem.
Sanov’s Theorem
Sanov’s asks how likely is it that the empirical distribution some IIDRV’s is far from the distribution. And shows that the relative entropy determines the likelihood of being far.
Entropy and Boltzmann’s Distribution
Entropy and Relative Entropy occur sufficiently often in these notes to justify a (somewhat) self-contained section. We cover the discrete case which is the most intuitive.